NDVI
NDVI Imagery That Puts You In Control Of Your Fields
Monitor your fields and stay ahead of crop issues with NDVI satellite imagery — complete overview from anywhere:
- Optimize input use and reduce waste
- Detect crop stress and nutrient deficiencies remotely
- Pinpoint problem areas and take action fast
- Plan data-backed harvesting schedules
What is NDVI
Think of NDVI as a "Greenness Meter" for your crops, using pictures taken from satellites or drones. It's a simple tool that shows you the health and vigor of your plants, across your entire field, in a single image.
- Healthy plants are smart. They absorb most of the red light from the sun to use for photosynthesis (that's why they look green to us).
- At the same time, their leaf structure reflects most of the near-infrared light (a type of light our eyes can't see).
- The more red light a plant absorbs (and the more infrared light it reflects), the healthier and more active it is.
- NDVI just measures this difference and gives you a number and a color-coded map.
How "WHY Crop Monitoring" turns satellite imagery into actionable NDVI
Collects gigabytes of raw data from several satellites daily
Processes imagery to detect and filter out clouded and shadowed
Delivers cloud-free NDVI-processed satellite imagery on the WHY Super app
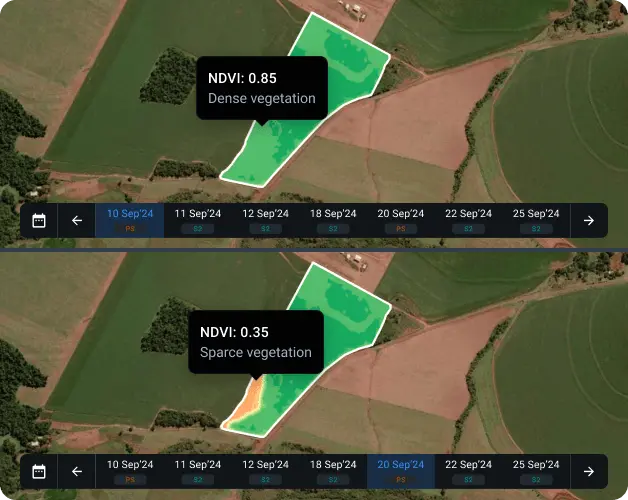
Detecting and fixing crop issues early through NDVI change alerts
With NDVI change alerts, the farmer detected crop stress early and preserved both yield quantity and grain quality — avoiding costly crop losses.

Identifying low-productivity areas with year-to-year NDVI comparisons
Consistently low index readings over several growing seasons often point to problems like poor drainage, unsuitable soil pH, low nutrient levels, or soil compaction. Reviewing NDVI imagery from past seasons allows farmers to pinpoint underperforming areas and refine their management strategies for the next seasons.
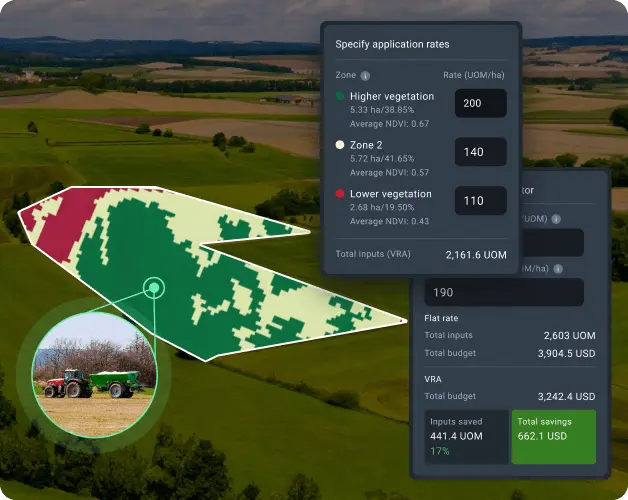
NDVI-powered variable rate input application
NDVI imagery allows agriculture producers to apply fertilizer where it will actually work. Through detailed imagery analysis, farmers distinguish between high-vigor areas with strong growth potential and low-potential areas with limited response capacity. Rather than treating fields uniformly, NDVI-guided application concentrates fertilizer in high-response zones while reducing waste in areas where additional inputs won't translate to yield.
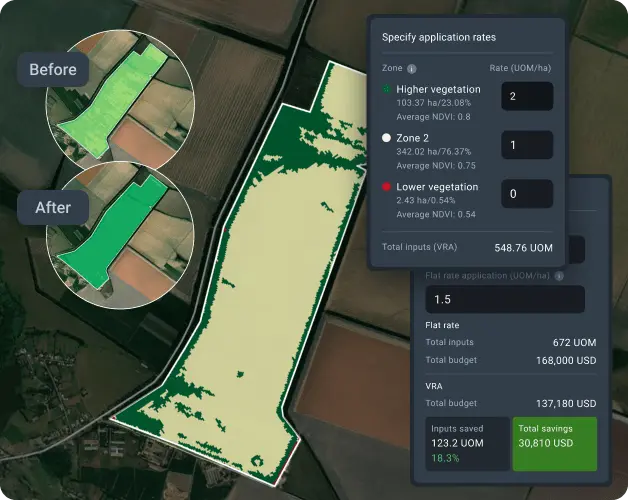
Cost-efficient plant growth regulation with NDVI mapping
NDVI imagery revealed the exact wheat growth zones, which let the farmer implement zone-specific PGR rates: higher doses for areas with strong growth that tend to lodge, lower doses for areas with moderate growth, and no application for areas that are struggling. Our platform's algorithms transformed NDVI imagery into maps for download and use on agriculture machinery to apply plant growth regulators precisely. This not only synchronized plant development and yield consistency throughout the field but also eliminated wasteful and harmful over-application.
With NDVI crop monitoring, the wheat grower achieved the most consistent crop maturity and harvest quality in his farming history while reducing PGR costs and chemical load on the environment.
Why choose NDVI imagery on WHY Crop Monitoring?
Several imagery providers: Sentinel-2 and PlanetScope
Updates daily with PlanetScope and every 3–5 days with Sentinel-2
High-resolution (3m) imagery from PlanetScope
Reliable cloud-detection algorithm
10+ vegetation indices available for deeper insights
Built-in NDVI-driven tools to inform better farming decisions
Smooth integration with weather, soil moisture, and other key data sources
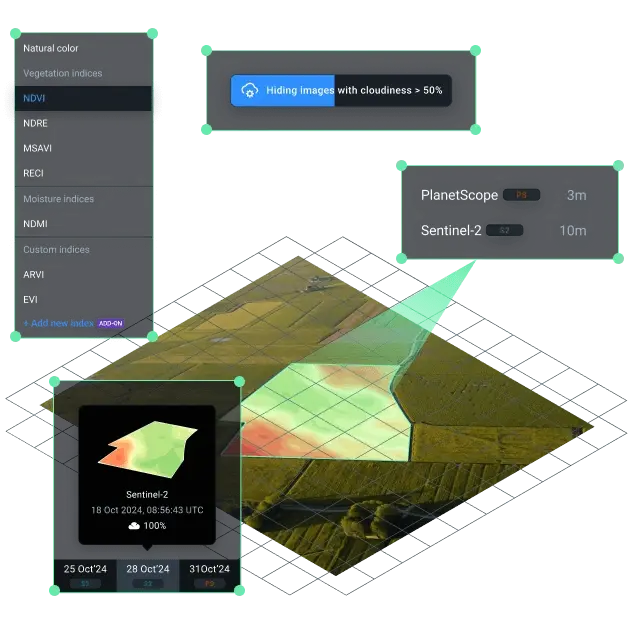
Go beyond NDVI with smart index selection
NDVI works great for precision agriculture, but occasionally it just isn't the best fit for a crop's current growth stage. If this happens, our algorithm recommends the most relevant index. Check out other readily available vegetation indices
NDMI
REcI
NDRE
NDMI
NDSI
MSAVI
GNDVI
NDSI